3D printing is an emerging technology in the field of manufacturing, which is called "manufacturing technology with the significance of industrial revolution". In recent years, with the progress of industrial technology, 3D printing technology has been rapidly developed and widely concerned by the media. All kinds of 3D printing technology have been reported one after another.
Next, I would like to share with you the principles of 3D printing polymer and metal. It mainly introduces the five polymer technologies of SLA, CLIP, 3DP, PolyJet and FDM, and the five metal 3D printing principles of NPJ, SLM, SLS, LMD and EBM.
SLA, or photocuring molding technology, refers to the molding method that uses ultraviolet light to irradiate liquid photosensitive resin to undergo polymerization reaction to cure layer by layer and generate three-dimensional entity. The workpiece prepared by SLA has high scale accuracy, which is the earliest commercialized 3D printing technology.
The following is SLA process engineering:

Ultraviolet laser source
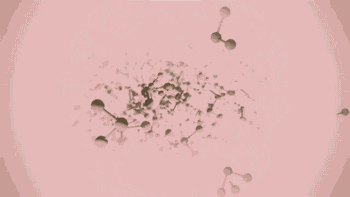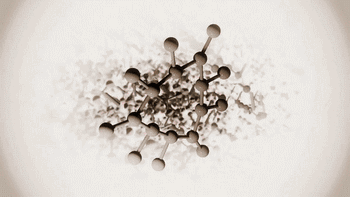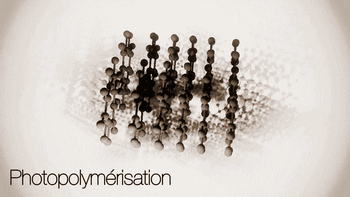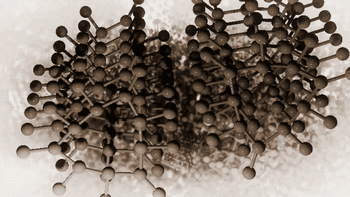
Photocuring reaction
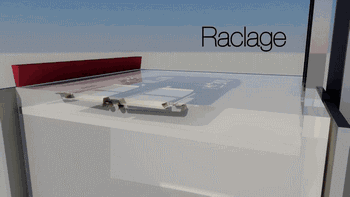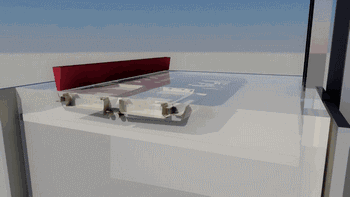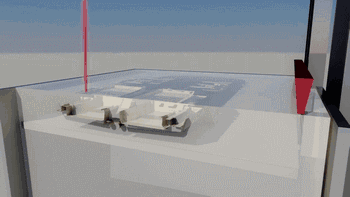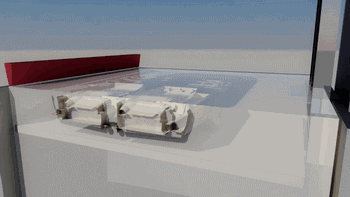
Layer by layer scanning molding
CLIP, Continuous Liquid Interface Extraction technology, is a revolutionary 3D printing technology developed on the basis of SLA technology by Carbon 3D, which increases the speed of 3D printing by 100 times!
The CLIP is projected from the bottom to cure the photosensitive resin. The parts that do not need curing are controlled by oxygen, forming dead zones, inhibiting the photocuring reaction and maintaining a stable liquid region, thus ensuring the continuity of curing.
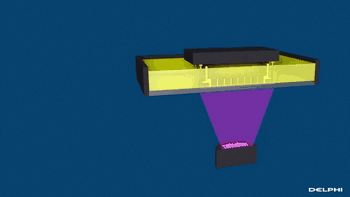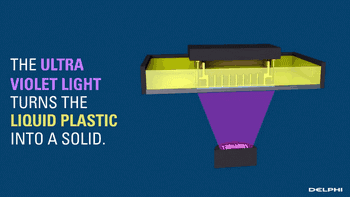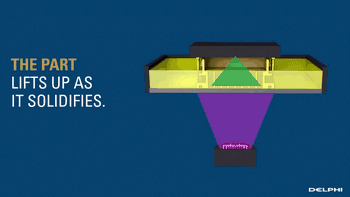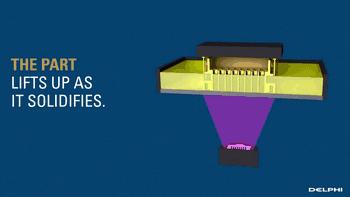
Photocuring reaction
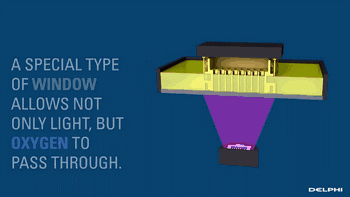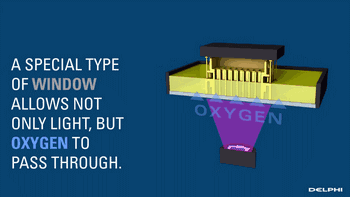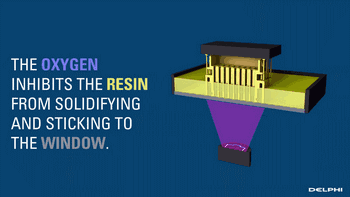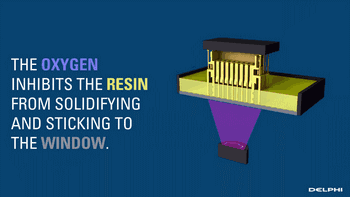
Oxygen inhibits the photocuring process

Photocuring dead zone demonstration
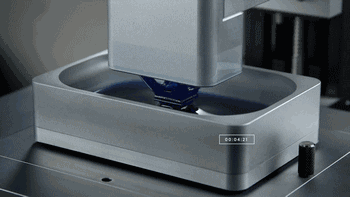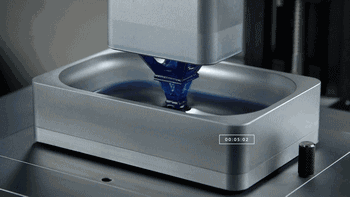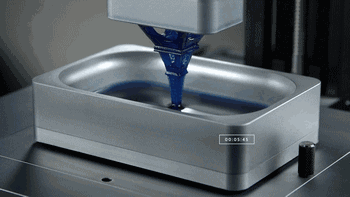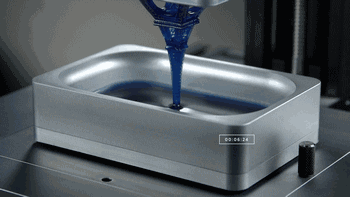
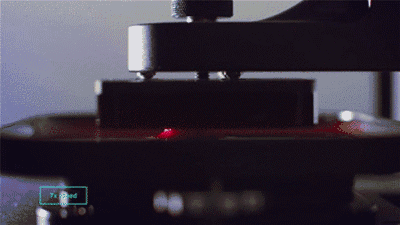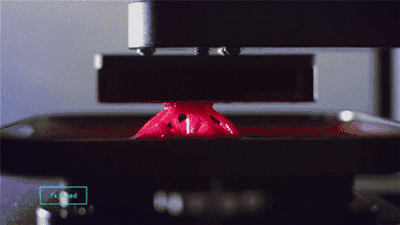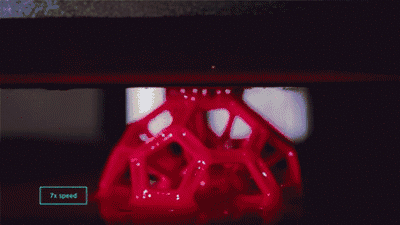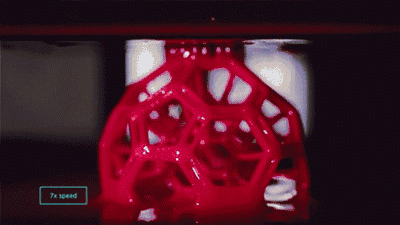
CLIP forming process
3DP is three-dimensional printing rapid prototyping technology, which is similar to the traditional two-dimensional inkjet printing, ejecting binder from the nozzle (color binder can print color parts), bonding the powder on the platform to form, usually using gypsum powder as the forming material. 3DP technology currently has two main applications: full color 3D printing and sand casting.
Here's how Exone uses 3DP for sand casting:

Binder ejection

Heat curing
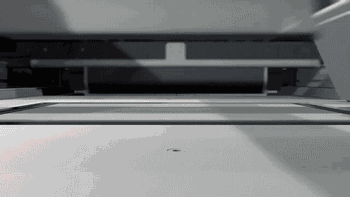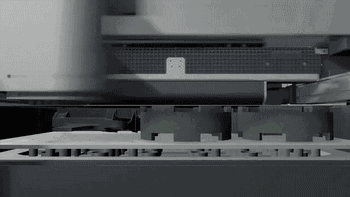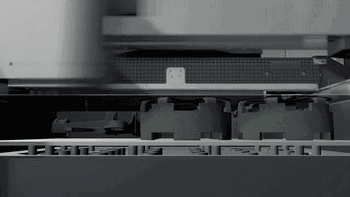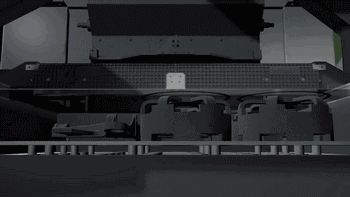
Print molding
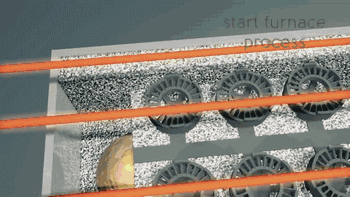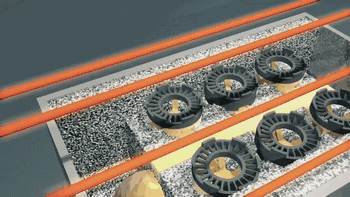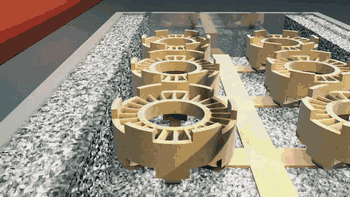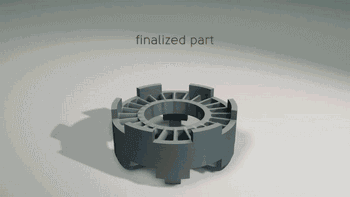
Casting molding
PolyJet, or polymer injection technology, is shaped in a similar way to 3DP, but instead of a binder, it jets a photocurable resin, which is then solidified by ultraviolet light.
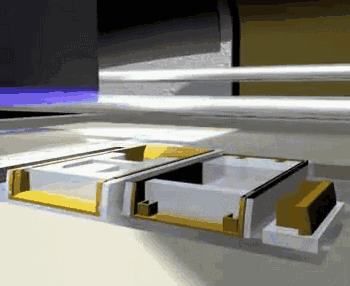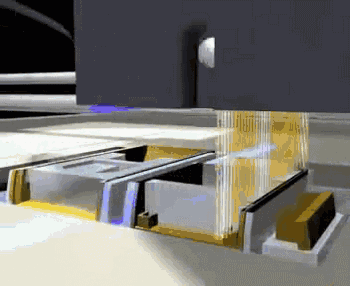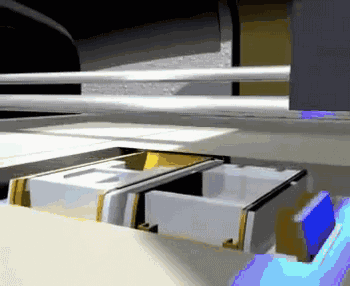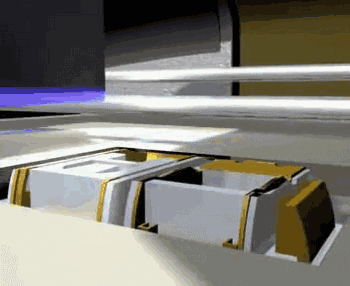
PolyJet forming principle
PolyJet uses an array nozzle that can even spray different materials at the same time, enabling simultaneous printing of multiple materials and multi-color materials.
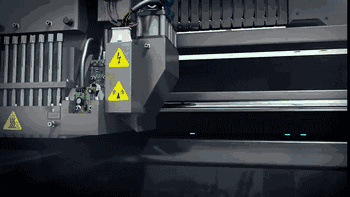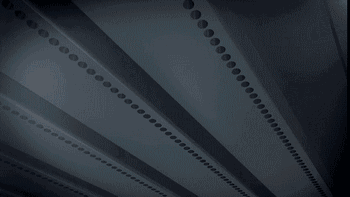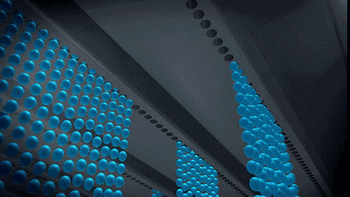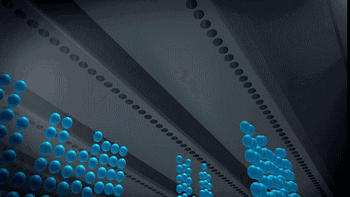
Working process of array nozzle

PolyJet printing process
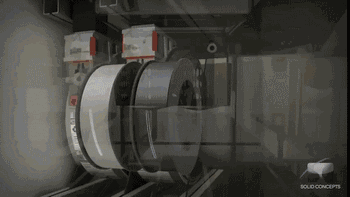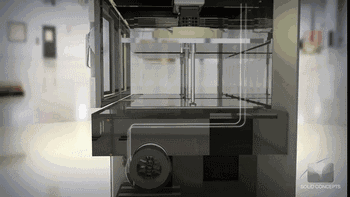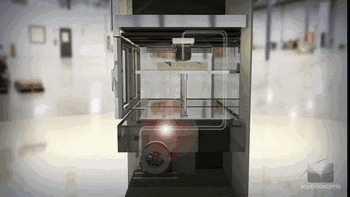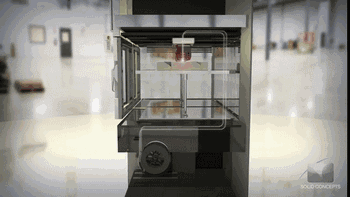
FDM is fusion stratification technology, the use of high temperature to melt the material, through the print head extrusion into a fine wire, in the component platform accumulation forming. FDM is the simplest and most common 3D printing technology and is commonly used in desktop 3D printing devices.
Here's how FDM technology works:

Model processing
Consumable extrusion forming

Layer by layer printing process

Removal of support

Surface treatment
Metal 3D printing technology can be directly used in the rapid prototyping manufacturing of metal parts, has broad industrial application prospects, is the focus of development at home and abroad of 3D printing technology, the following to share with you NPJ, SLM, SLS, LMD and EBM five metal 3D printing principles.
NPJ technology is the latest metal 3D printing forming technology developed by Xjet, an Israeli company. Compared with ordinary laser 3D printing, NPJ uses nano liquid metal, which is deposited and formed in the way of inkjet. The printing speed is 5 times faster than ordinary laser printing, and it has excellent accuracy and surface roughness.
Here's how the Xjet device works:
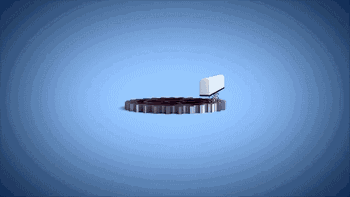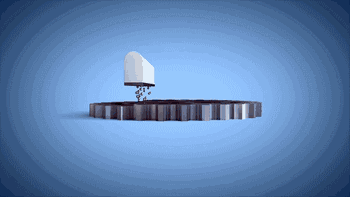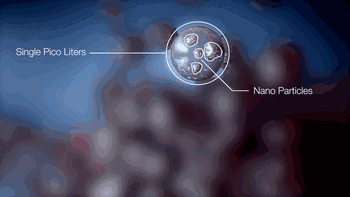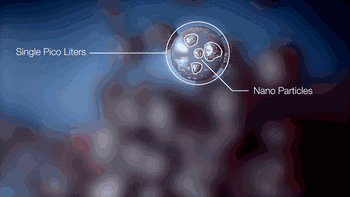
Metal particles are distributed in the droplet
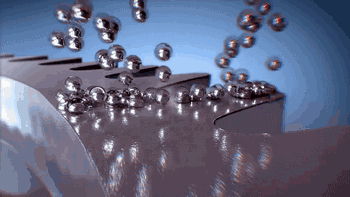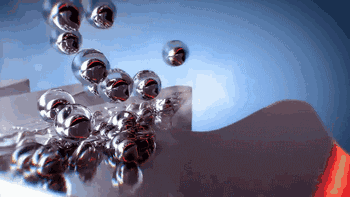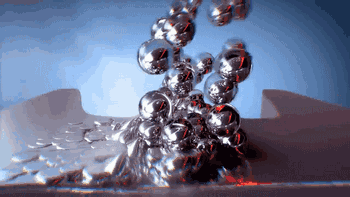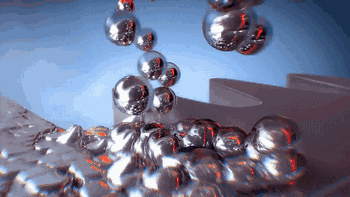
Droplet injection molding process

Liquid phase expulsion process
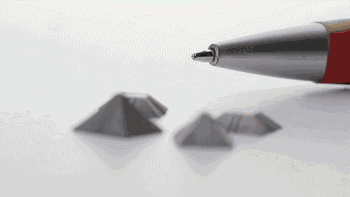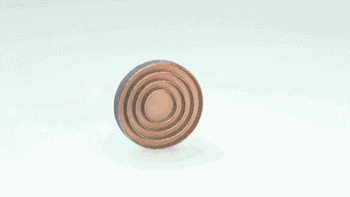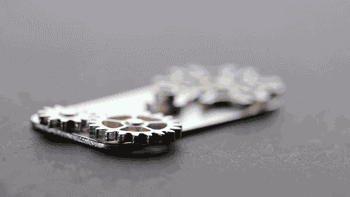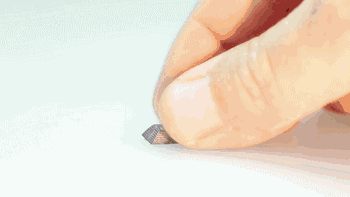
Sintered parts
SLM is the selective laser melting forming technology, which is the most common technology in metal 3D printing. It adopts fine focusing spot to melt preset metal powder quickly, and directly obtains the parts with arbitrary shape and complete metallurgical combination. The resulting production density can reach more than 99%.
Laser galvanometer system is one of the key technologies of SLM. The following is the working diagram of the galvanometer system of SLM Solution Company:
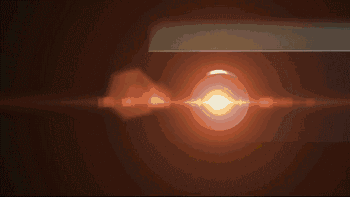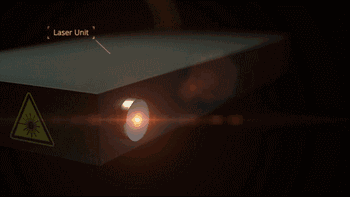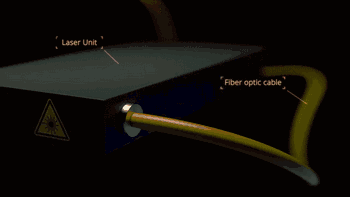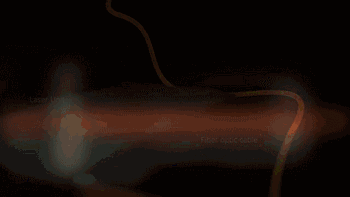
Laser emission

Laser transmission

Scanning galvanometer

Laser scanning fusion
Metal powder melting process
In the process of metal 3D printing, supporting materials need to be printed because of the complexity of the workpiece. After the workpiece is finished, the supporting materials need to be removed and the surface of the workpiece needs to be treated.

Take out parts

Removal of support

post-processing
SLS is the selective laser sintering technology, similar to SLM technology, the difference is that the laser power is different, usually used in polymer 3D printing molding.
Here's how SLS prepares plastic parts:

Model stratified slice

Laser sintering process

Removal of parts

post-processing
SLS can also be used to make metal or ceramic parts, but the resulting parts have low density and require a late densification process before they can be used.

SLS makes metal parts
LMD is laser cladding forming technology, which has a variety of names and has been independently researched and named by different research institutions. Common names include LENS, DMD, DLF, LRF, etc. The biggest difference with SLM is that its powder is gathered on the work surface through the nozzle and is fused with the laser at one point. The powder is melted and cooled to obtain the accumulated cladding entity.
Here's how the LENS technology works:
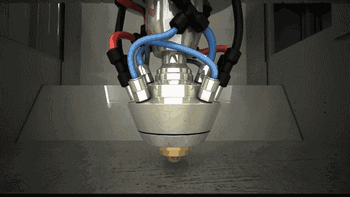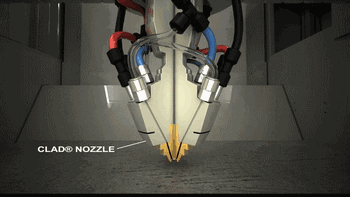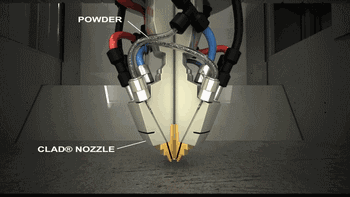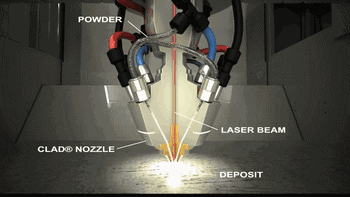
Coaxial powder feeding

Construction process
EBM is electron beam melting technology, its process is very similar to SLM, the difference is that EBM uses the energy source of the electron beam. The electron beam output energy of EBM is usually an order of magnitude larger than the laser output power of SLM, and the scanning speed is also much higher than that of SLM. Therefore, in the construction process of EBM, the whole modeling table needs to be preheated to prevent large residual stress caused by excessive temperature in the forming process.
The following is the EBM working process:
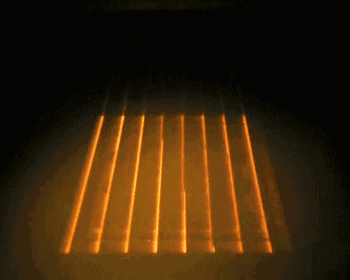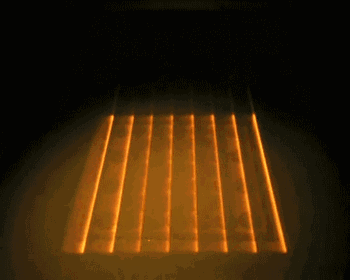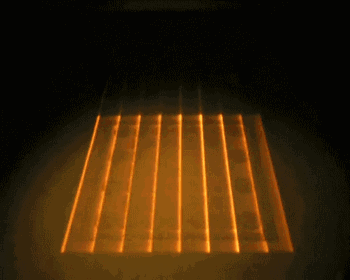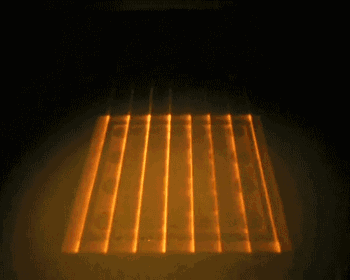
Integral preheating
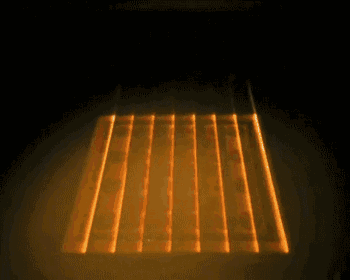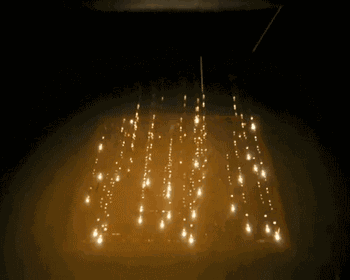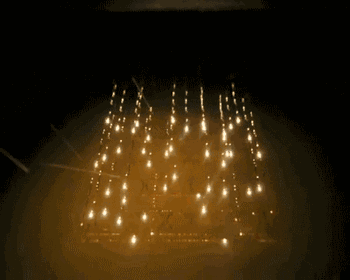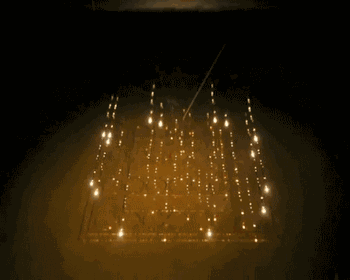

Forming process

The change of powder during melting
--- END ---